A linked list a data structure for storing a collection of data elements. The elements in the collection can be of any data type such as int, char, float etc., Linked lists store each data elements inside a node. A node consists of 2 fields - a data field which stores the actual data and pointer field which contains a pointer to the next node. So the first node (the node on the top of the list) contains some data and a pointer to the second node. The second node also contains some data and a pointer to the third node and so on. The last node in the list will point to NULL. A the pointer to the node at the top of the list is called head pointer. Here is an an example.
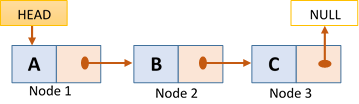
The linked list described above is also knows as a singly linked list as it has a single pointer that points to the next node. There are also other types of linked lists such as a doubly linked list which has pointers to both previous and next nodes.
Here is a C Program to perform the following operations on a singly linked list.
- Add new elements to the top of the list.
- Display all elements in the list.
- Count the number of nodes in the list.
- Remove all occurances of an element from the list.
This program also displays a menu for the users to make a selection. Here is the full source code.
Source Code
/*************************************************
* C program to add, remove, count and *
* print the elements in a linked list *
*************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
/* Node Stucture */
typedef struct node_t {
int data;
struct node_t *next;
} Node;
/* Function Declarations */
Node * add(int, Node *);
Node * remove(int, Node *);
void print(Node *);
int count(Node *);
/* Add a new node to linked list */
Node * add(int num, Node *head) {
Node *new_node;
new_node = (Node *) malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node->data = num;
new_node->next= head;
head = new_node;
return head;
}
/* Print all the elements in the linked list */
void print(Node *head) {
Node *current_node = head;
while ( current_node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", current_node->data);
current_node = current_node->next;
}
}
/* Count the number of nodes in a linked list */
int count(Node *head) {
int cnt = 0;
Node *current_node = head;
while ( current_node != NULL) {
cnt++;
current_node = current_node->next;
}
return(cnt);
}
/* Remove an element from a linked list */
Node * remove(int num, Node *head) {
Node *current_node = head;
Node *prev_node;
int cnt = 0;
while ( current_node != NULL) {
if (current_node->data == num) {
if (current_node == head) {
head = current_node->next;
} else {
prev_node->next = current_node->next;
}
}
prev_node = current_node;
current_node = current_node->next;
}
return(head);
}
/* Program main */
int main()
{
Node *head = NULL;
int num;
int option;
char * temp;
/* Display Menu */
while(1) {
printf("\n ******************************************\n");
printf("\n * Linked list operations: *\n");
printf("\n * 1. Add *\n");
printf("\n * 2. Remove *\n");
printf("\n * 3. Count *\n");
printf("\n * 4. Print *\n");
printf("\n * 5. Quit *\n");
printf("\n ******************************************\n");
printf("\n Choose an option [1-5] : ");
if (scanf("%d", &option) != 1) {
printf(" *Error: Invalid input. Press try again.\n");
scanf("%s", &temp); /*this will clear the input buffer */
continue;
}
switch (option) {
case 1: /* Add */
printf(" Enter a number to add : ");
if (scanf("%d", &num) != 1) {
printf(" *Error: Invalid input. Only integer numbers are allowed\n");
scanf("%s", &temp); /*this will clear the input buffer */
continue;
}
head = add(num, head);
printf("Number %d is now added to the list", num);
printf("\nPress any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
case 2: /* Remove */
printf(" Enter a number to remove : ");
if (scanf("%d", &num) != 1) {
printf(" *Error: Invalid input. Only integer numbers are allowed\n");
scanf("%s", &temp); /*this will clear the input buffer */
continue;
}
head = remove(num, head);
printf("Number %d is now removed from the list", num);
printf("\nPress any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
case 3: /* Count */
printf("\nYour linked list contains %d nodes", count(head));
printf("\nPress any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
case 4: /* Print */
printf("\nYour linked list contains the following values: \n [ ");
print(head);
printf("]\n\nPress any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
case 5: /* Exit */
return(0);
break;
default:
printf("Invalid Option. Please Try again.");
getch();
} /* End of Switch */
} /* End of While */
return(0);
}


